October 25, 2020
Nutrition & Immunity


Here’s the bottom line folks. If you eat well, chances are your body will work well. So, the next time you see enthusiastic health claims related to ‘boosting your immune system with nutrition’ or ‘the secrets to immunity building with diets’ take a deep breath and head first to the produce section of your supermarket. ( More to come on that as we scroll onward!)

Of course, there are nutrients in the foods we eat and beverages we drink that play important roles in providing what’s needed for the body to fight off infections and yes, even pesky viruses. But as we like to say in science based nutrition advice, “There are NO magic foods, drinks or potions that specifically reign supreme as the white knight saving the disease fighting day.” You may quote me.
But, immunolgists doing the front line research in humans (vivo) and in the lab (vitro) are identifying meal patterns that support a healthy immune system. These meal patterns and in some cases dietary supplements provide nutrients that work as the tiny tools to help fight the bad bugs causing the trouble and to feed the body’s fighter cells such as T-cells. More on that next!

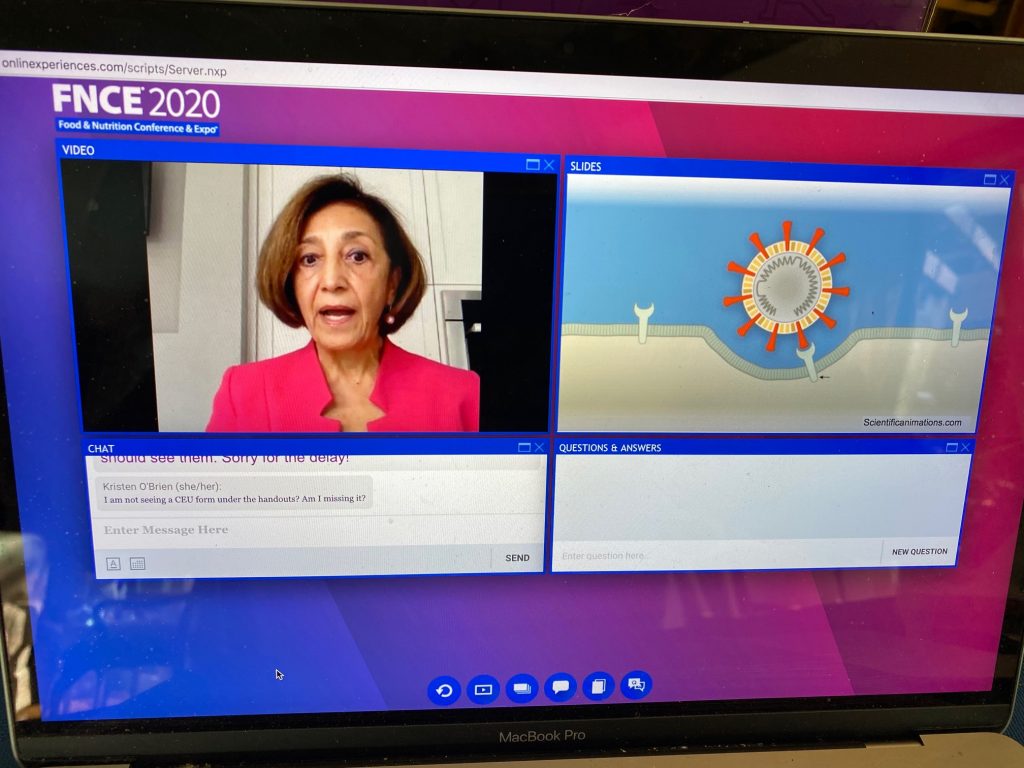
Immunologist Simin Meydani, Ph.D. of Tufts University recently presented information on Nutrition & Immunity, with specific attention to fighting the Covid-19 virus, at the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics annual Food & Nutrition Conference. Here are my notes based on her presentation.
Simin Meydani, PhD Senior Scientist & Director Nutritional Immunology Lab, USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts
Covid Fighting Nutrients in the Science Supported News
Keep in mind that a lot of this is based on extrapolation from other non-covid related research and a lot of the promising mechanisms have been observed in lab studies, not in actual patients. I’ll make special note if it’s connected to observed health improvements in humans.
Topping the list:
Any nutrient that acts as an antioxidant such as vitamin E and vitamin C.
Because viruses can reduce the level of inflammation-fighting antioxidants it makes sense we’d need more in a time of crisis. Viruses also tamp down levels of vitamin D. So ditto.
Vitamin E: Human study showed that giving patients 600 IU of vitamin E for 6 weeks helped reduce the inflammation markers called cytokines. If someone is in a full blown inflammatory response to disease it is often called a “cytokine storm”.
Zinc: The mineral zinc appears to help the immune system specifically by supporting disease fighting T-cells. A zinc deficiency is associated with higher rates of infection (with longer duration and more resistance to antibiotics) and even loss of taste and smell. (Hello! That’s one of the theories why one of the symptoms of Covid-19 is loss of taste and smell). A human study where older subjects were given 45 mg/day of zinc for a year, showed the subjects had lower rates of infection with shorter duration of colds. Even 30mg/day of supplemental zinc has shown to increase T-cell production.
Vitamin D: Immune response research shows that low levels of vitamin D3 is associated with higher risk of upper respiratory infections. We are all supposed to be taking a vitamin D supplement, especially if you avoid the sun or are over age 65.
Vitamin C: “Our immune cells gobble up vitamin C”, says Dr. Meydani. So it’s wise to up vitamin C intake during an active response to disease. Those who already have low vitamin C status in their body’s serum levels seem to benefit the most. Some folks need even more vitamin C than the recommended 60-100 mg per day, including smokers and those fighting disease or healing from surgery or an injury.
There’s a trend in medical and non-medical use of IV vitamin C infusions. Often used when serum levels are deficient. But, Dr. Meydani says “There’s no published evidence of benefits of IV vitamin C use in Covid patients.”

EASY TO EAT ENOUGH VITAMIN C: The best dietary sources of vitamin C are citrus fruits, strawberries, and even green bell peppers. Gobble them up!
Quercetin: Intriguing emerging lab research that the flavonoid quercetin found naturally in plants such as apples and onions might work to block the attachement of the covid virus’s spikes to the exterior of the body’s cells, thereby preventing the entry of the virus into the human cell.

Quercetin also shown in lab studies to block the increase of cytokine production therefore helping to prevent inflammation.
Dietary sources of quercetin: Apples, onions, green tea, grapes, broccoli, berries, capers, coffee and red wine.
Another reason to eat “an apple a day”!

A Important Note on Obesity: Adipose tissue impairs T-cell production and therefore the body’s immune response. This is another reason that obesity is associated with ill health and specifically in Covid-19 patients, obesity is associated with a higher use of artificial ventilation in hospitalization. Dr. Meydani says it’s not just the BMI or the weight on the scales, “It’s the adipose tissue itself where the inflammation happens.” Muscle weight is not associated with impaired T-cells. Good news from mice studies though; adding more fruits and vegetables to the diet increased T-cell production even in obese mice.

In summary, eat your vegetables. And remember that before taking higher doses beyond the RDA for any nutrients supplements you should check for a deficiency first.
Nutrition makes a difference!